Cache
Midscene.js provides AI caching features to improve the stability and speed of the entire AI execution process. The cache mainly refers to caching how AI recognizes page elements. Cached AI query results are used if page elements haven't changed.
Instructions
Currently, the caching capability is supported in all scenarios, and Midscene can support file-level caching.
Usage
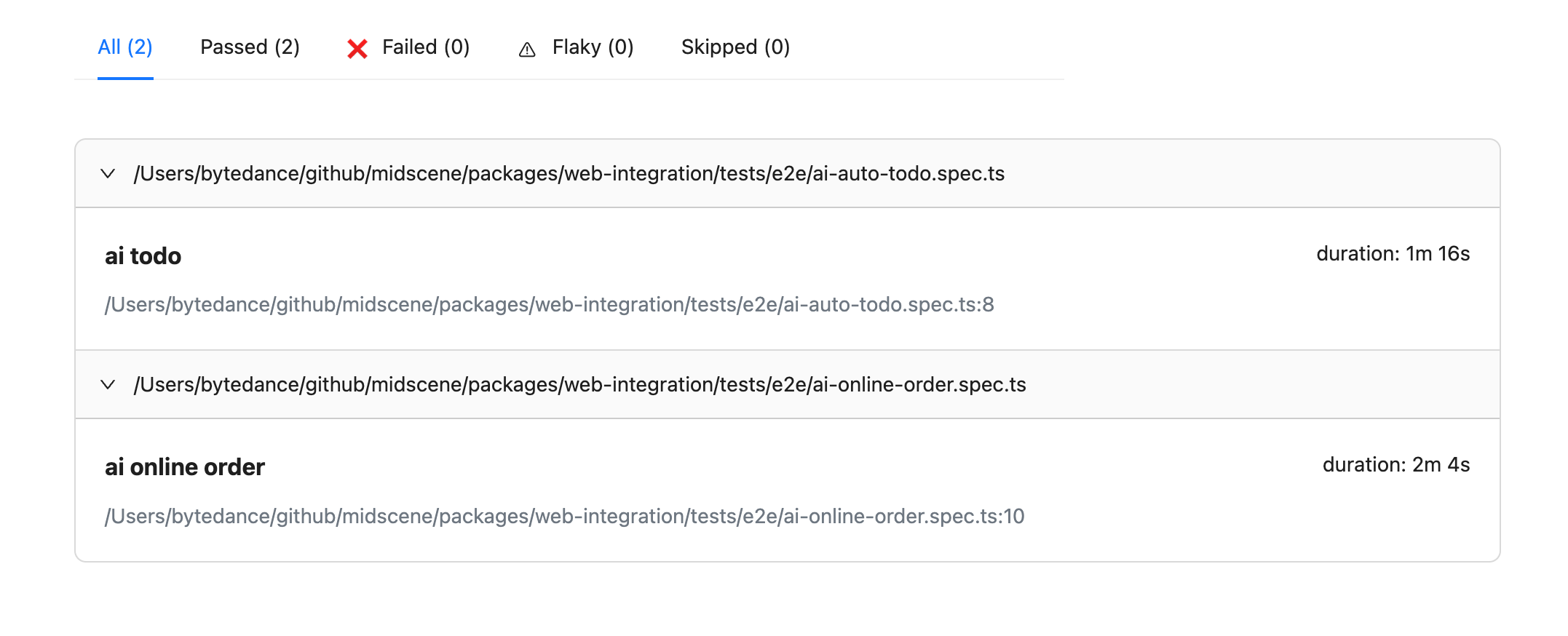
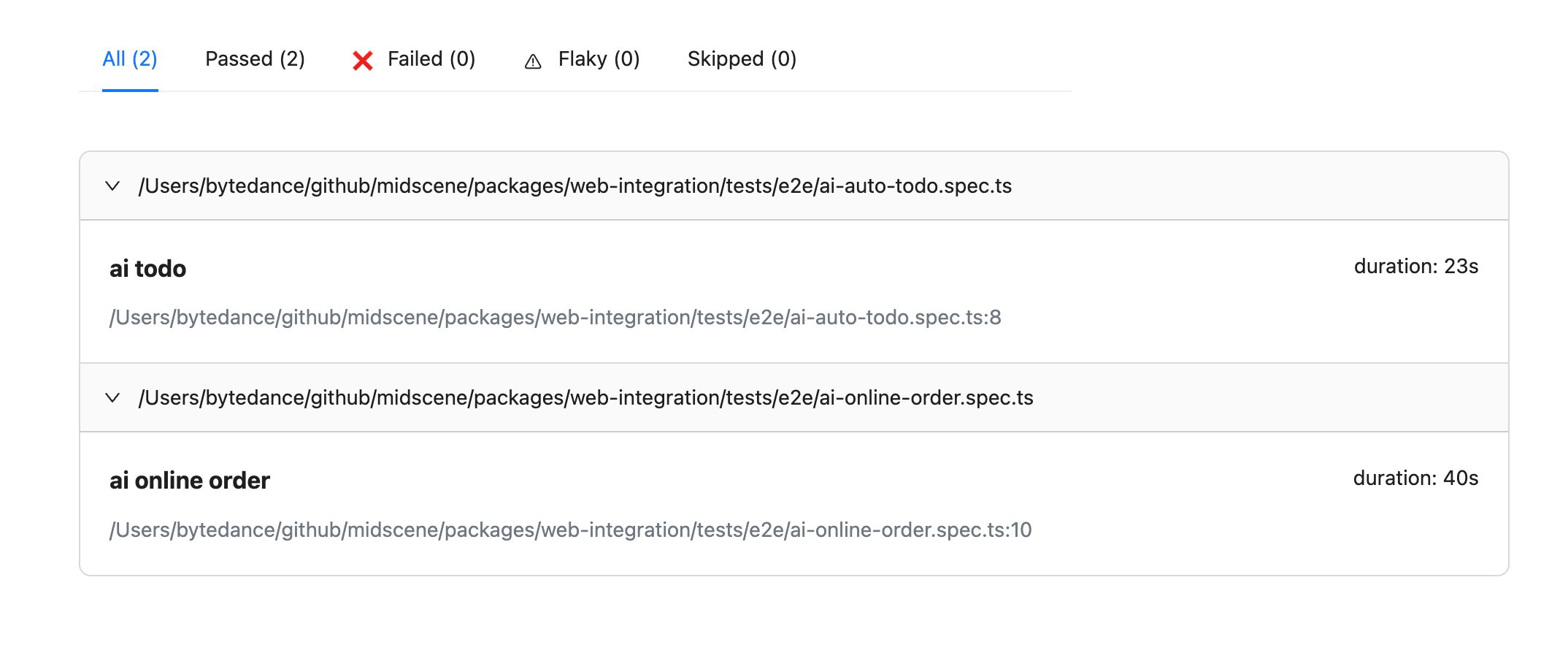
Effect
After enabling the cache, the execution time is significantly reduced, for example, from 1m16s to 23s.
- before
- after
Cache Content
Currently, Midscene's caching strategy in all scenarios is mainly based on the test file unit. AI behavior in each test file will be cached. The cached content is mainly divided into two categories:
- AI's planning for tasks (Planning, i.e., the results of ai and aiAction methods)
- AI's recognition of elements
The content of aiQuery will not be cached, so you can use aiQuery to confirm whether the previous AI tasks meet expectations.
Task Planning
The above task planning will be decomposed into:
When the URL address and page width and height have not changed, enabling the cache will directly cache the results of the above tasks.
Element Recognition
After the AI has planned the user's instructions into tasks, it needs to operate on specific elements, so the AI's element recognition capability is needed. For example, the following task:
The above element recognition will be converted into specific element recognition:
Cache Strategy
When using the MIDSCENE_CACHE=true environment variable, caching will be automatically performed according to Playwright's test groups:
The above test will generate caches along the dimensions of ai todo and ai todo2, and todo-mvc.spec.ts-1.json and todo-mvc.spec.ts-2.json cache files will be generated in the midscene/midscene_run/cache directory in the project root.
Cache File Introduction
When the MIDSCENE_CACHE=true environment variable is used and there are cache files, the AI's corresponding results will be read through the above cache file. The following are the conditions for cache hit:
- The same test file and test title
- Midscene package name, version, and last task are consistent
- The page address and page width and height where the corresponding task is executed are consistent
- The current page has exactly the same elements as last time (only required for locate element tasks)
Common Issues
Why provide caching capability?
The caching capability mainly solves the following problems:
- High AI response latency, a task will take several seconds, and when there are dozens or even hundreds of tasks, there will be a higher latency
- AI response stability, through training and experiments, we found that GPT-4 has an accuracy rate of over 95% in page element recognition tasks, but it cannot reach 100% accuracy yet. The caching capability can effectively reduce online stability issues
What happens if the cache is not hit?
For AI behaviors that do not hit the cache, they will be re-executed by AI, and the cache will be updated after the entire test group is executed. You can check the cache file to determine which tasks have been updated.
How to manually remove the cache?
- When deleting the corresponding cache file, the cache of the entire test group will automatically become invalid
- When deleting specific tasks in the cache file, the corresponding tasks will automatically become invalid. Deleting the tasks before will not affect the tasks after. The tasks will be updated after successful execution

