缓存
Midscene.js 提供了 AI 缓存能力,用于提升整个 AI 执行过程的稳定性和速度。这里的缓存主要指的是缓存 AI 识别页面的元素,在页面元素尚未发生变化时,AI 的查询结果会被缓存。
使用说明
目前缓存的能力在所有场景下都进行了支持,Midscene 能够支持文件级别的缓存。
使用方式
使用效果
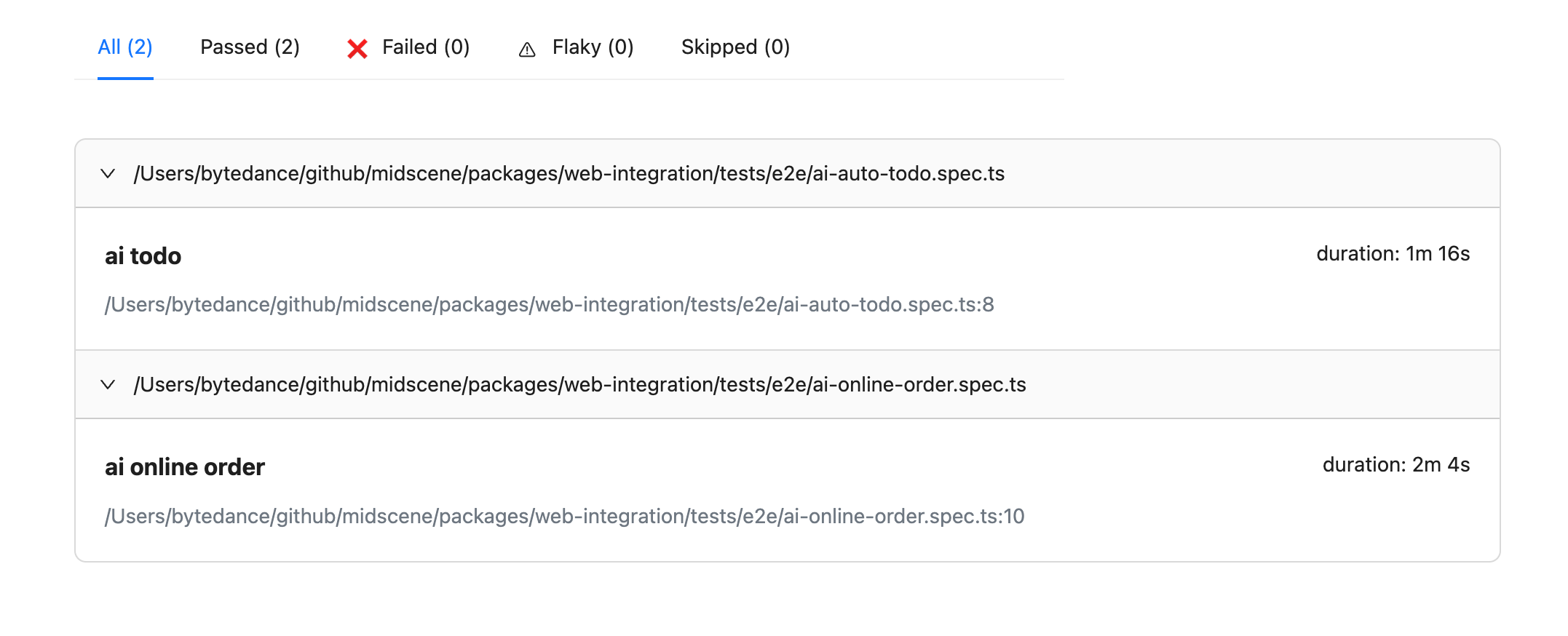
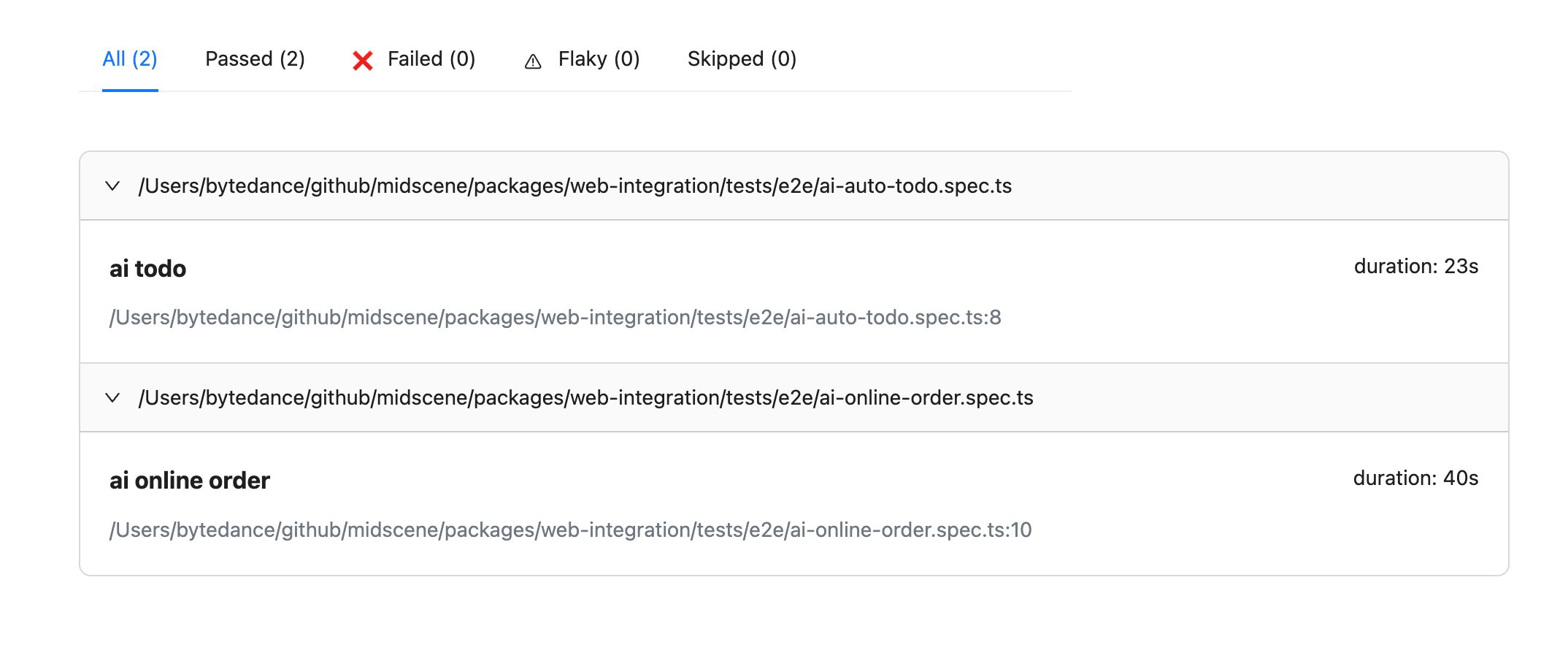
通过引入缓存后,用例的执行时间大幅降低了,例如从1分16秒降低到了23秒。
- before
- after
缓存内容
目前 Midscene 在所有场景下的缓存策略主要是以测试文件为单位,在每个测试文件里的 AI 行为将发生缓存。目前缓存的内容主要有两类:
- AI 对于任务的规划(Planning, 即 ai 和 aiAction 方法的结果)
- AI 对于元素的识别
不会对 aiQuery 的内容进行缓存,因此可以通过 aiQuery 来确认前面 AI 的任务是否符合预期。
任务规划
上面的任务规划将会被拆解成:
当页面的 URL 地址和页面的宽高未发生变化时,开启缓存后将会直接缓存上面任务的结果。
元素识别
在 AI 对用户的指令进行了任务规划后,需要针对特定的元素进行操作,那么就需要用到 AI 对于页面元素的识别能力,例如下面的任务:
上面的元素识别将会转换成具体的元素识别:
缓存策略
当使用 MIDSCENE_CACHE=true 环境变量后,将会自动按照 Playwright 的测试组进行缓存:
上面的 test 将按照 ai todo 和 ai todo2 这两个维度产生缓存,分别会在项目的根目录中的 midscene/midscene_run/cache 中生成 todo-mvc.spec.ts-1.json 和 todo-mvc.spec.ts-2.json 缓存文件。
缓存文件介绍
当使用了 MIDSCENE_CACHE=true 环境变量并且有缓存文件时,将会通过上面的缓存文件读取 AI 对应的结果。以下是缓存命中的条件:
- 相同的测试文件和测试标题
- Midscene 包名、版本和上次的任务一致
- 对应任务执行的页面地址、页面宽高一致
- 当前页面存在和上次一模一样的元素(仅针对定位元素任务要求)
常见问题
为什么要提供缓存能力?
缓存能力主要解决了以下问题:
- AI 响应延迟高,一个任务将会耗费几秒钟,当有几十条甚至几百条任务时将会有较高的耗时
- AI 响应稳定性,通过调教和实验中我们发现 GPT-4 在页面元素识别的任务上有 95%+ 的准确率,但尚无法达到 100% 的准确率,通过缓存能力能够有效降低线上稳定性问题
未命中缓存会发生什么?
对于未命中缓存的 AI 行为将会交给 AI 重新执行任务,并在整个测试组执行结束后更新缓存,可以通过查看缓存文件来确定哪些任务是否有更新。
如何手动去掉缓存?
- 删除对应的缓存文件时,整个测试组的缓存将会自动失效
- 删除缓存文件里面特定的任务时,对应的任务将会自动失效,任务执行成功后将会更新任务,删除前面的任务不会影响后面的任务
