Android Getting Started
This guide walks you through everything required to automate an Android device with Midscene: connect a real phone over adb, configure model credentials, try the no-code Playground, and run your first JavaScript script.
Set up API keys for model
Set your model configs into the environment variables. You may refer to Model strategy for more details.
export MIDSCENE_MODEL_BASE_URL="https://replace-with-your-model-service-url/v1"
export MIDSCENE_MODEL_API_KEY="replace-with-your-api-key"
export MIDSCENE_MODEL_NAME="replace-with-your-model-name"
export MIDSCENE_MODEL_FAMILY="replace-with-your-model-family"
For more configuration details, please refer to Model strategy and Model configuration.
Prepare your Android device
Before scripting, confirm adb can talk to your device and the device trusts your machine.
Install adb and set ANDROID_HOME
Example output indicates success:
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 34.0.4-10411341
Installed as /usr/local/bin//adb
Running on Darwin 24.3.0 (arm64)
Any non-empty output means it is configured:
/Users/your_username/Library/Android/sdk
Enable USB debugging and verify the device
In the system settings developer options, enable USB debugging (and USB debugging (Security settings) if present), then connect the device via USB.
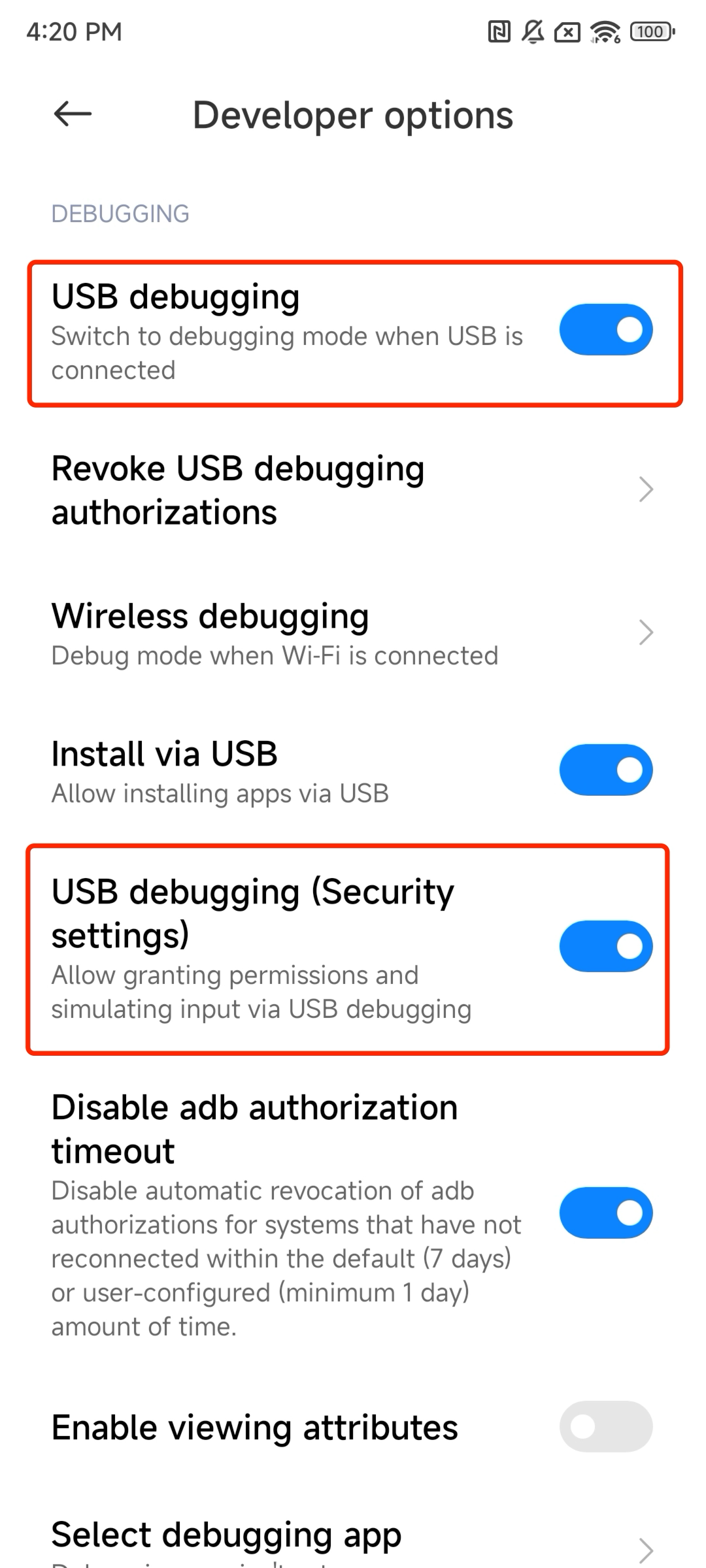
Verify the connection:
Example success output:
List of devices attached
s4ey59 device usb:34603008X product:cezanne model:M2006J device:cezan transport_id:3
Try Playground (no code)
Playground is the fastest way to validate the connection and observe AI-driven steps without writing code. It shares the same core as @midscene/android, so anything that works here will behave the same once scripted.
- Launch the Playground CLI:
npx --yes @midscene/android-playground
- Click the gear icon in the Playground window, then paste your API key configuration. Refer back to Model configuration if you still need credentials.
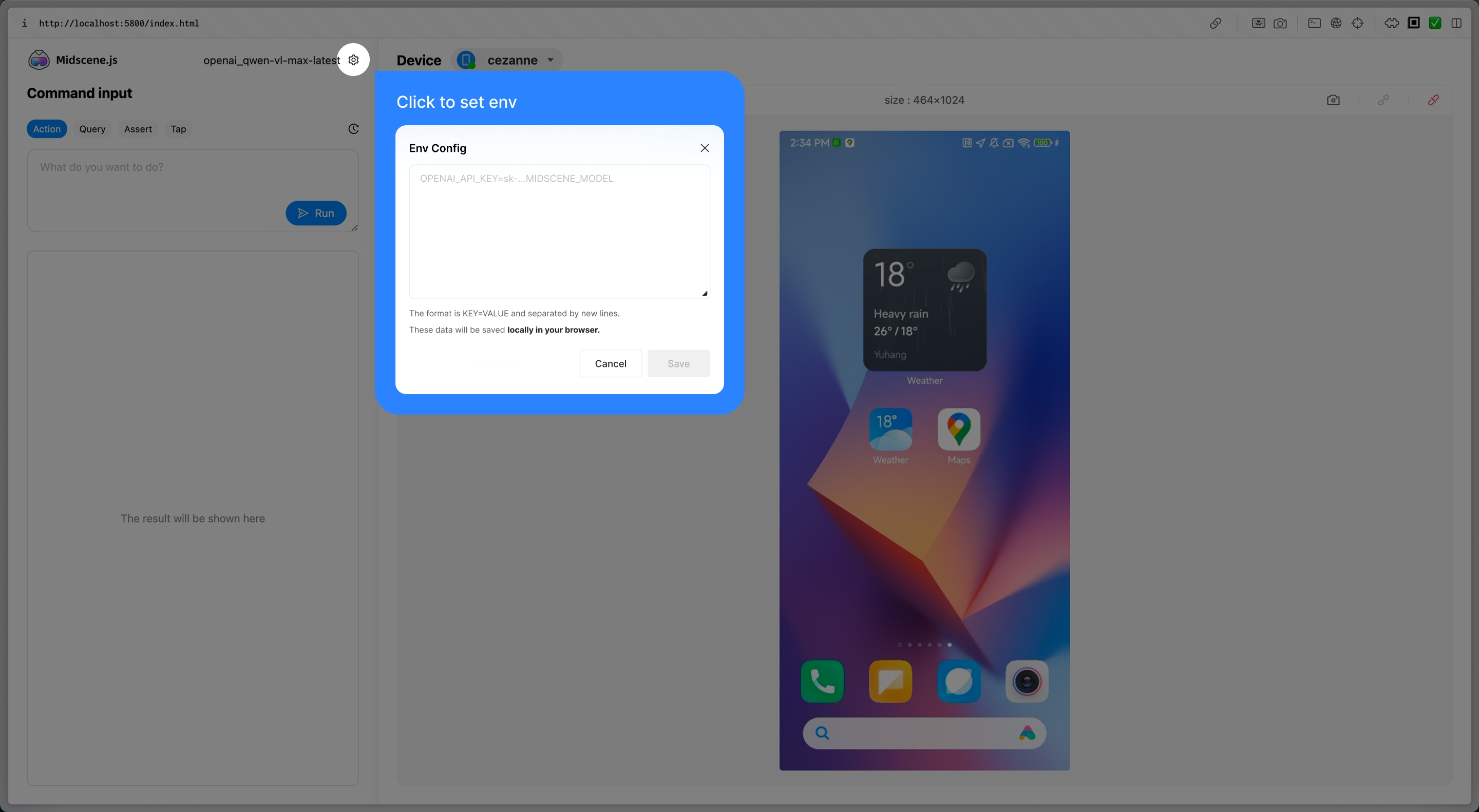
Start experiencing
After configuration, you can start using Midscene right away. It provides several key operation tabs:
- Act: interact with the page. This is Auto Planning, corresponding to
aiAct. For example:
Type “Midscene” in the search box, run the search, and open the first result
Fill out the registration form and make sure every field passes validation
- Query: extract JSON data from the interface, corresponding to
aiQuery.
Similar methods include aiBoolean(), aiNumber(), and aiString() for directly extracting booleans, numbers, and strings.
Extract the user ID from the page and return JSON data in the { id: string } structure
- Assert: understand the page and assert; if the condition is not met, throw an error, corresponding to
aiAssert.
There is a login button on the page, with a user agreement link below it
- Tap: click on an element. This is Instant Action, corresponding to
aiTap.
For the difference between Auto Planning and Instant Action, see the API document.
Integration with Midscene Agent
Once Playground works, move to a repeatable script with the JavaScript SDK.
Step 1. Install dependencies
npm install @midscene/android --save-dev
yarn add @midscene/android --save-dev
pnpm add @midscene/android --save-dev
bun add @midscene/android --save-dev
deno add npm:@midscene/android --save-dev
Step 2. Write scripts
Save the following code as ./demo.ts. It opens the browser on the device, searches eBay, and asserts the result list.
./demo.ts
import {
AndroidAgent,
AndroidDevice,
getConnectedDevices,
} from '@midscene/android';
const sleep = (ms) => new Promise((r) => setTimeout(r, ms));
Promise.resolve(
(async () => {
const devices = await getConnectedDevices();
const device = new AndroidDevice(devices[0].udid);
const agent = new AndroidAgent(device, {
aiActionContext:
'If any location, permission, user agreement, etc. popup, click agree. If login page pops up, close it.',
});
await device.connect();
await agent.aiAct('open browser and navigate to ebay.com');
await sleep(5000);
await agent.aiAct('type "Headphones" in search box, hit Enter');
await agent.aiWaitFor('There is at least one headphone product');
const items = await agent.aiQuery(
'{itemTitle: string, price: Number}[], find item in list and corresponding price',
);
console.log('headphones in stock', items);
await agent.aiAssert('There is a category filter on the left');
})(),
);
Step 3. Run
Step 4: View the report
Successful runs print Midscene - report file updated: /path/to/report/some_id.html. Open the generated HTML file in a browser to replay every interaction, query, and assertion.
Advanced
Use this section when you need to customize device behavior, wire Midscene into your framework, or troubleshoot adb issues. For detailed constructor parameters, jump to the API reference(Android).
Extend Midscene on Android
Use defineAction() for custom gestures and pass them through customActions. Midscene will append them to the planner so AI can call your domain-specific action names.
import { getMidsceneLocationSchema, z } from '@midscene/core';
import { defineAction } from '@midscene/core/device';
import { AndroidAgent, AndroidDevice, getConnectedDevices } from '@midscene/android';
const ContinuousClick = defineAction({
name: 'continuousClick',
description: 'Click the same target repeatedly',
paramSchema: z.object({
locate: getMidsceneLocationSchema(),
count: z.number().int().positive().describe('How many times to click'),
}),
async call(param) {
const { locate, count } = param;
console.log('click target center', locate.center);
console.log('click count', count);
},
});
const devices = await getConnectedDevices();
const device = new AndroidDevice(devices[0].udid);
await device.connect();
const agent = new AndroidAgent(device, {
customActions: [ContinuousClick],
});
await agent.aiAct('click the red button five times');
See Integrate with any interface for a deeper explanation of custom actions and action schemas.
More
Complete example (Vitest + AndroidAgent)
import {
AndroidAgent,
AndroidDevice,
getConnectedDevices,
} from '@midscene/android';
import type { TestStatus } from '@midscene/core';
import { ReportMergingTool } from '@midscene/core/report';
import { sleep } from '@midscene/core/utils';
import type ADB from 'appium-adb';
import {
afterAll,
afterEach,
beforeAll,
beforeEach,
describe,
it,
} from 'vitest';
describe('Android Settings Test', () => {
let page: AndroidDevice;
let adb: ADB;
let agent: AndroidAgent;
let startTime: number;
let itTestStatus: TestStatus = 'passed';
const reportMergingTool = new ReportMergingTool();
beforeAll(async () => {
const devices = await getConnectedDevices();
page = new AndroidDevice(devices[0].udid);
adb = await page.getAdb();
});
beforeEach((ctx) => {
startTime = performance.now();
agent = new AndroidAgent(page, {
groupName: ctx.task.name,
});
});
afterEach((ctx) => {
if (ctx.task.result?.state === 'pass') {
itTestStatus = 'passed';
} else if (ctx.task.result?.state === 'skip') {
itTestStatus = 'skipped';
} else if (ctx.task.result?.errors?.[0].message.includes('timed out')) {
itTestStatus = 'timedOut';
} else {
itTestStatus = 'failed';
}
reportMergingTool.append({
reportFilePath: agent.reportFile as string,
reportAttributes: {
testId: `${ctx.task.name}`,
testTitle: `${ctx.task.name}`,
testDescription: 'description',
testDuration: (Date.now() - ctx.task.result?.startTime!) | 0,
testStatus: itTestStatus,
},
});
});
afterAll(() => {
reportMergingTool.mergeReports('my-android-setting-test-report');
});
it('toggle wlan', async () => {
await adb.shell('input keyevent KEYCODE_HOME');
await sleep(1000);
await adb.shell('am start -n com.android.settings/.Settings');
await sleep(1000);
await agent.aiAct('find and enter WLAN setting');
await agent.aiAct(
'toggle WLAN status *once*, if WLAN is off pls turn it on, otherwise turn it off.',
);
});
it('toggle bluetooth', async () => {
await adb.shell('input keyevent KEYCODE_HOME');
await sleep(1000);
await adb.shell('am start -n com.android.settings/.Settings');
await sleep(1000);
await agent.aiAct('find and enter bluetooth setting');
await agent.aiAct(
'toggle bluetooth status *once*, if bluetooth is off pls turn it on, otherwise turn it off.',
);
});
});
Tip
Merged reports are stored inside midscene_run/report by default. Override the directory with MIDSCENE_RUN_DIR when running in CI.
FAQ
Why can't I control the device even though I've connected it?
A common error is:
Error:
Exception occurred while executing 'tap':
java.lang.SecurityException: Injecting input events requires the caller (or the source of the instrumentation, if any) to have the INJECT_EVENTS permission.
Make sure USB debugging is enabled and the device is unlocked in developer options.

How do I use a custom adb path or remote adb server?
Set the environment variables first:
export MIDSCENE_ADB_PATH=/path/to/adb
export MIDSCENE_ADB_REMOTE_HOST=192.168.1.100
export MIDSCENE_ADB_REMOTE_PORT=5037
You can also provide the same information via the constructor:
const device = new AndroidDevice('s4ey59', {
androidAdbPath: '/path/to/adb',
remoteAdbHost: '192.168.1.100',
remoteAdbPort: 5037,
});




