Use JavaScript to optimize the AI automation code
Many developers love using ai or aiAction to accomplish complex tasks, and even describe all logic in a single natural language instruction. Although it may seem 'intelligent', in practice, this approach may not provide a reliable and efficient experience, and results in an endless loop of Prompt tuning.
Here is a typical example, developers may write a large logic storm with long descriptions, such as:
Another common misconception is that the complex workflow can be effectively controlled using aiAction methods. These prompts are far from reliable when compared to traditional JavaScript. For example:
One path to optimize the automation code: use JavaScript and structured API
From v0.16.10, Midscene provides data extraction methods like aiBoolean aiString aiNumber, which can be used to control the workflow.
Combining them with the instant action methods, like aiTap, aiInput, aiScroll, aiHover, etc., you can split complex logic into multiple steps to improve the stability of the automation code.
Let's take the first bad case above, you can convert the .aiAction method into a structured API call:
Original prompt:
Converted code:
After modifying the coding style, the whole process can be much more reliable and easier to maintain.
A more complex example
Here is another example, this is what it looks like before rewriting:
After using the structured APIs, developers can easily inspect the code step by step.
Commonly-used structured API methods
Here are some commonly-used structured API methods:
aiBoolean - conditional decision
- Use Case: Condition Judgment, State Detection
- Advantage: Convert fuzzy descriptions into clear boolean values
Example:
aiString - text extraction
- Use Case: Text Content Retrieval
- Advantage: Avoid Ambiguity in Natural Language Descriptions
Example:
aiNumber - numerical extraction
- Use Case: Counting, Numerical Comparison, Loop Control
- Advantage: Ensure Return Standard Numeric Types
Example:
aiQuery - general data extraction
- Use Case: Extract any data type
- Advantage: Flexible Data Type Handling
Example:
Instant action methods
Midscene provides some instant action methods, like aiTap, aiInput, aiScroll, aiHover, etc., They are also commonly used in the automation code. You can check them in the API page.
Want to write structured code easily?
If you think the javascript code is hard to write, then this is the right time to use the AI IDE.
Use your AI IDE to index the following documents:
- https://midscenejs.com/blog-programming-practice-using-structured-api.md
- https://midscenejs.com/api.md
How to add the Midscene documents to the AI IDE?
Refer to this article.
And use this prompt with the mention of the Midscene documents:
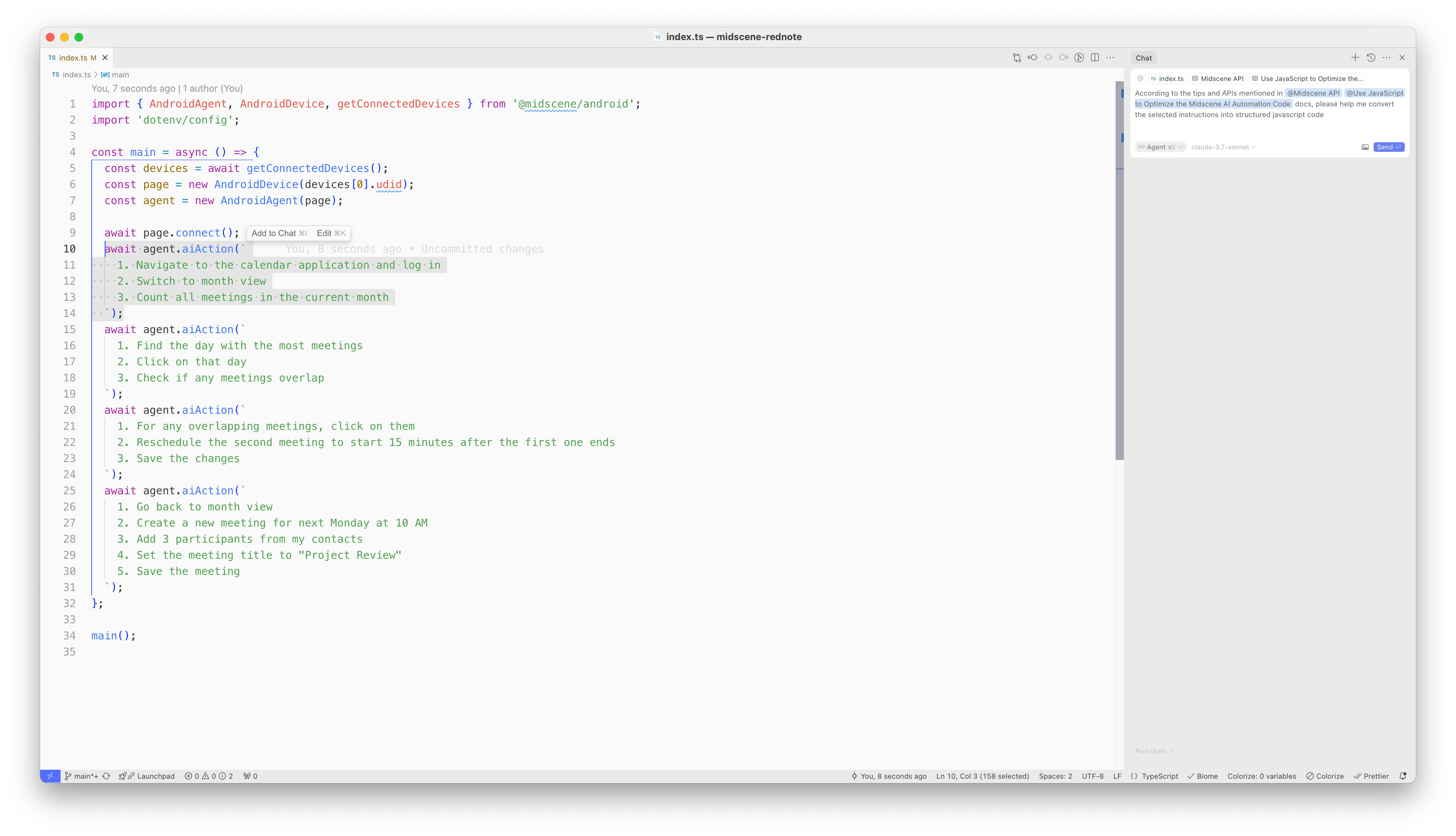
After you input the prompt, the AI IDE will convert the prompt into structured javascript code:
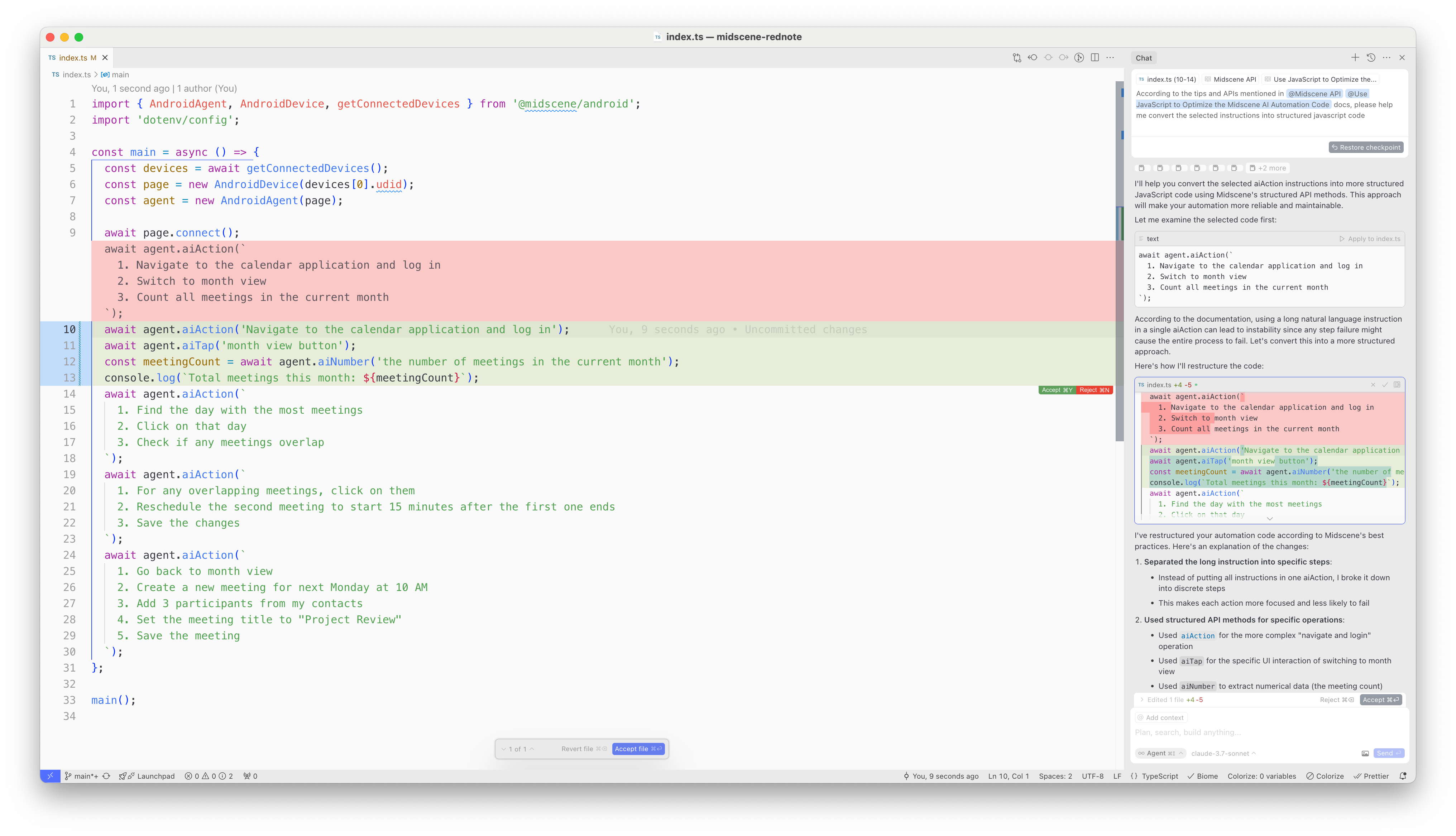
Enjoy it!
Which approach is best: aiAction or structured code?
There is no standard answer. It depends on the model's ability, the complexity of the actual business.
Generally, if you encounter the following situations, you should consider abandoning the aiAction method:
- The success rate of
aiActiondoes not meet the requirements after multiple retries - You have already felt tired and spent too much time repeatedly tuning the
aiActionprompt - You need to debug the script step by step
What's next?
To achieve better performance, you can check the Midscene caching feature to cache the planning and xpath results.
To learn more about the structured API, you can check the API reference.

